High memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10 or 11 can slow down your computer. When you see 100% memory usage in Task Manager, it means your system is running out of RAM. This can cause programs to lag, freeze, or even crash. A common reason for this problem is Google Chrome, a popular web browser that often uses a lot of RAM and CPU, especially if you keep many tabs open or use several extensions.
This article explains why your memory usage is high and how to fix it. You’ll learn simple steps to reduce RAM usage, like closing tabs or updating software. For a long-term solution, upgrading your RAM is recommended. Most users need at least 8GB of RAM, but 16GB DDR4 at 3200MHz is better for smooth performance. Whether you’re a casual user or a multitasker, this guide has clear answers to help you.
What Is High Memory Usage in Task Manager?
High memory usage in Task Manager means your computer’s RAM is nearly full. RAM is the memory your system uses to run programs like Chrome or games. When Task Manager shows 100% usage, your computer struggles to keep up with your tasks.
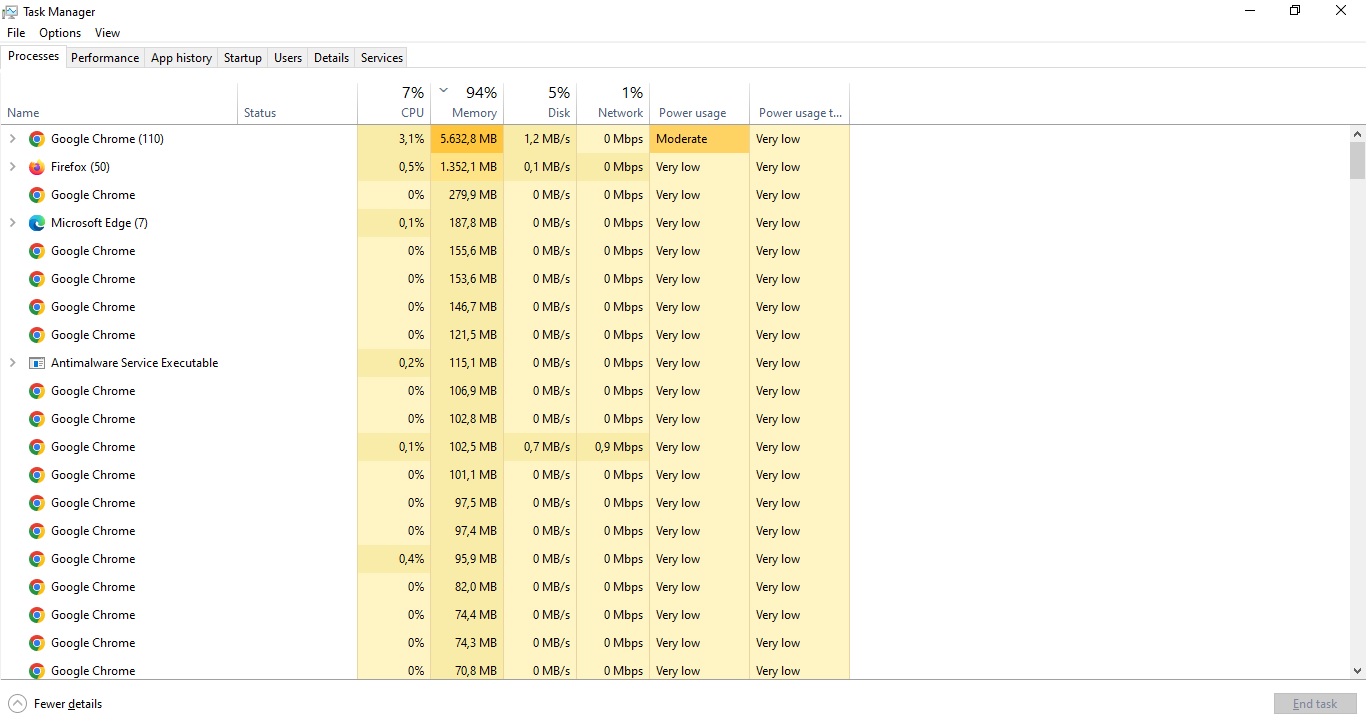
To check this, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager. Click the “Performance” tab, and look at the “Memory” section. You’ll see a percentage and a graph. If it’s at or near 100%, your RAM is maxed out. This can happen when you have too many programs open or when one program, like Chrome, uses more memory than your system can handle.
High usage isn’t always bad—Windows tries to use all available RAM to speed things up. But when it hits 100%, your computer may slow down. For example, opening a new tab might take longer, or your game might stutter. Knowing what causes this is the first step to fixing it.
What Does RAM Do in Windows 10 and 11?
RAM stores data for the programs you’re using right now. It’s short-term memory that helps your computer work fast. When you open Chrome, write a document in Word Office, or stream YouTube, RAM holds that information so your system can access it quickly.
In Windows 10 and 11, RAM works with your processor to run everything smoothly. The more RAM you have, the more tasks your computer can handle at once. For instance, with 4GB of RAM, you might struggle to browse and stream video together. With 16GB, you can do that and more without issues.
You can see how much RAM you have in Task Manager under the “Performance” tab. It also shows how much is in use. If you often see high usage, your RAM might not be enough for your needs. Let’s explore why Chrome pushes it to the limit.
Why Does Google Chrome Use So Much Memory?
Google Chrome uses a lot of memory because of its multi-process design. Each tab and extension runs as a separate process. This keeps Chrome stable; if one tab crashes, others stay open. But it also means more RAM is used. The more tabs you open, so Google Chrome consumes your RAM.
Here are the main reasons Chrome takes up so much RAM:
- Multiple Processes: Every open tab uses its own memory. For example, 10 tabs might use 1-2GB of RAM total, depending on the websites you visit.
- Extensions: Add-ons like ad blockers or Grammarly use extra memory. Even when idle, they add to Chrome’s RAM usage.
- Preloading: Chrome loads parts of webpages before you visit them to make browsing faster. This uses more RAM upfront.
Chrome’s design improves speed and safety, but it can overload your system. If you have 10 tabs, 5 extensions, and stream a video, your RAM fills up fast. Next, we’ll look at how to manage this.

How Can You Reduce High Memory Usage on Windows?
You can reduce high memory usage on your Windows 10/11 with simple steps or by upgrading your RAM. Here are 5 practical solutions to lower Chrome’s RAM use and keep your system running smoothly.
Close Unnecessary Tabs and Extensions
Closing tabs and extensions frees up RAM quickly. Each tab in Chrome uses memory, even if it’s just sitting there. Extensions, like grammar checkers or VPNs, also take up space.
- Go through your tabs and close the ones you don’t need. Right-click a tab and select “Close.”
- To manage extensions, type
chrome://extensions/in the address bar. Turn off or remove extras by toggling the switch or clicking “Remove.”
For example, closing 7 unused tabs might save 700MB of RAM. Also, Fewer extensions mean less background usage on your Windows.
Update Chrome and Windows
Updating software fixes bugs that cause high memory usage. New versions of Chrome and Windows often use RAM more efficiently. You can close all browsing activity and then update Chrome. This method is quite effective in reducing RAM usage on your laptop. How to do? Follow the tips below:
- For Chrome: Type
chrome://settings/helpand click “Check for updates.” Install any available updates. - For Windows: Go to “Settings” > “Update & Security” > “Windows Update” and click “Check for updates.”
Updates can reduce memory leaks—when programs hold onto RAM they don’t need. Check for updates monthly to stay current.
Adjust Chrome Settings
Changing Chrome settings can lower its memory use. One key option is hardware acceleration, which uses your graphics card but sometimes increases RAM usage.
- Type
chrome://settings/systemin Chrome. - Toggle off “Use hardware acceleration when available” and restart Chrome.
This might slow some graphics-heavy sites, but it can save RAM. Test it to see if it helps your system.
End Processes in Task Manager
Ending processes in Task Manager stops programs from using too much RAM. If Chrome or another app is taking over, you can close it manually.
- Open Task Manager with Ctrl + Shift + Esc, or you can go to search and type ”task manager” then select it.
- Go to the “Processes” tab, find Chrome (it might list multiple entries), and click “End Task.”
Be careful—ending critical system processes can cause problems. Stick to closing Chrome or other apps you recognize.
Upgrade Your RAM
Upgrading RAM gives your computer more space to work. If the steps above aren’t enough, adding RAM is the best fix. For Windows 10/11, 8GB is the minimum, but 16GB DDR4 at 3200MHz is ideal for heavy Chrome users.
- Check your current RAM in Task Manager under “Performance” > “Memory.”
- Buy compatible RAM for your computer (check your manual or online).
- Install it yourself or get help from a tech expert.
More RAM means you can run Chrome, games, and other programs without hitting 100% usage. We’ll cover how to upgrade later.
How Do You Check and Manage Memory Usage?
You can check and manage memory usage with built-in Windows tools. Task Manager is the easiest, but others give more details.
- Task Manager: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc, go to “Performance,” and see your RAM usage in real-time.
- Resource Monitor: Type “Resource Monitor” in the Start menu. The “Memory” tab shows which programs use the most RAM.
- Windows Memory Diagnostic: Search for it in the Start menu to test if your RAM has errors.
For example, Resource Monitor might show Chrome using 2GB while a game uses 1GB. Close what you don’t need to free up space. These tools help you spot problems early.
How Do You Upgrade Your RAM?
Upgrading your RAM adds more memory to your computer. It’s a simple process if you follow these steps. Here’s how to do it:
- Check Your RAM: Open Task Manager, go to “Performance” > “Memory,” and note your current amount and type (e.g., DDR4).
- Find Compatible RAM: Look up your computer’s manual or model online to see how much RAM it supports and what type.
- Buy RAM: Get 8GB or 16GB DDR4 at 3200MHz for best results. Buy in pairs for better performance.
- Install It:
- Shut down and unplug your computer.
- Open the case (desktops) or RAM slot (laptops).
- Remove old RAM by pushing the clips and pulling it out.
- Insert new RAM until it clicks.
- Close everything up.
- Test It: Start your computer and check Task Manager to confirm the new RAM works.
If you’re unsure, take it to a tech shop. Upgrading to 16GB can stop 100% usage for good.
What Other Programs Cause High Memory Usage?
Other programs besides Chrome can use a lot of RAM. Here are some common ones:
- Video Editing Software: Tools like Adobe Premiere Pro use 4-8GB for big projects.
- Games: Titles like Call of Duty or Fortnite might need 6GB or more with high settings.
- Virtual Machines: Running Windows in VMware can take 2-4GB per instance.
- Background Apps: Antivirus or Dropbox sync might use 500MB or more.
Check Task Manager’s “Processes” tab to see what’s running. Close unnecessary programs to save RAM.
What Are Chrome’s Memory Management Tools?
Chrome has tools to help control its memory usage. Use these to keep RAM in check:
- Chrome Task Manager: Click the three dots, go to “More tools” > “Task Manager.” It shows memory use per tab and extension. End heavy ones by selecting and clicking “End Process.”
- Memory Saver: In
chrome://settings/performance, turn on “Memory Saver” to put inactive tabs to sleep. - Tab Discard: Chrome automatically drops unused tabs from memory. Reload them when needed.
For instance, closing a tab using 300MB in Chrome’s Task Manager frees that up instantly. These tools are built-in and easy to use.
FAQ
Can I Fix High Memory Usage Without Upgrading RAM?
Yes, you can fix it by managing Chrome and other programs. Closing tabs, disabling extensions, updating software, and ending processes in Task Manager reduce RAM use. For example, shutting 5 tabs might drop usage by 1GB.
Is 8GB RAM Enough for Windows 10/11?
Yes, 8GB works for basic tasks like browsing or streaming. But for multitasking—like running Chrome with more than 30 tabs and a game—16GB is better. It prevents slowdowns and keeps usage below 100%.
Does Closing Background Apps Reduce Memory Usage?
Yes, closing background apps frees up RAM. Apps like Skype or Spotify might use 200-500MB even when idle. End them in Task Manager or the system tray to give Chrome more room.
Conclusion
High memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10 or 11 can make your computer slow and frustrating. Google Chrome often causes this by using lots of RAM for its tabs, extensions, and preloading. You can lower usage by closing tabs, updating software, adjusting settings, or ending processes. These steps help, especially if you monitor usage with tools like Task Manager.
For a lasting fix, upgrading your RAM is the way to go. While 8GB is enough for most, 16GB DDR4 at 3200MHz handles heavy use better. It’s like giving your computer more space to breathe. With the right steps and enough RAM, you can stop seeing 100% usage and enjoy a faster system.